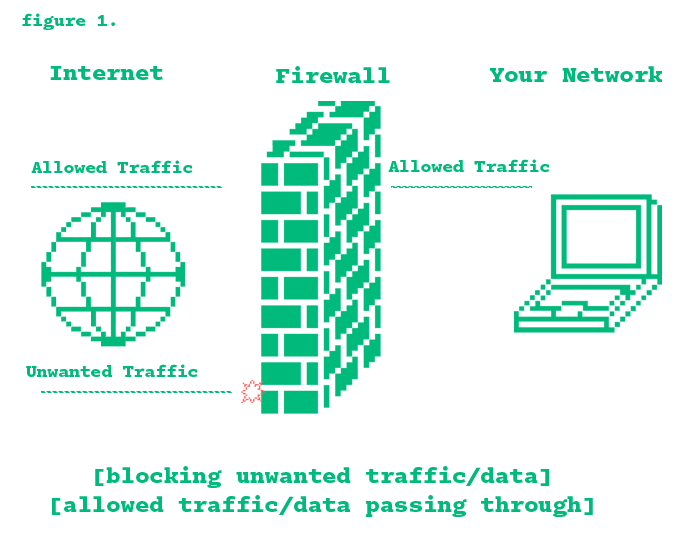
Network security systems like firewalls, IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems), and IPS (Intrusion Prevention Systems) work together
to protect your network. Firewalls filter incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules. IDS monitors network activity
to detect suspicious behavior and alerts administrators, while IPS goes a step further by actively blocking malicious traffic on
top of detecting it.
Firewalls are great at blocking unauthorized access, IDS helps identify potential threats, and IPS can stop attacks before
they cause harm. Together, they provide multi-layered defense for your network.
This site, bashbreach.com, actually uses some other security measures such as:
HTTPS
Protects data in transit between visitors and your website.
Prevents man-in-the-middle attacks where hackers could intercept sensitive information.
GitHub Pages General security
DDoS protection (since GitHub is backed by Cloudflare).
No direct access to servers, reducing attack vectors like SQL injection.
With these measures in place, bashbreach.com stays secure. I hope...
A firewall is a network security device that separates your internal network from an external network that might be deemed untrustworthy. Think of firewalls as a physical security gate in your house that decides what comes in and what doesn’t. It monitors incoming and outgoing traffic, based on protocols. Simply, firewalls examine and control traffic by allowing or denying it appropriately with pre-established security rules.
Think of firewalls as the TSA. They work as a checkpoint between you and the internet, they analyze data packets being sent
over the network, and then according to the rules they determine what's allowed and what isn’t, for your safety.
Firewalls do things like block unauthorized access while allowing legitimate traffic, filter data packets based on security
rules, prevent malware and hackers from exploiting vulnerabilities, and can be configured to allow or deny specific applications,
services, or IP addresses.1
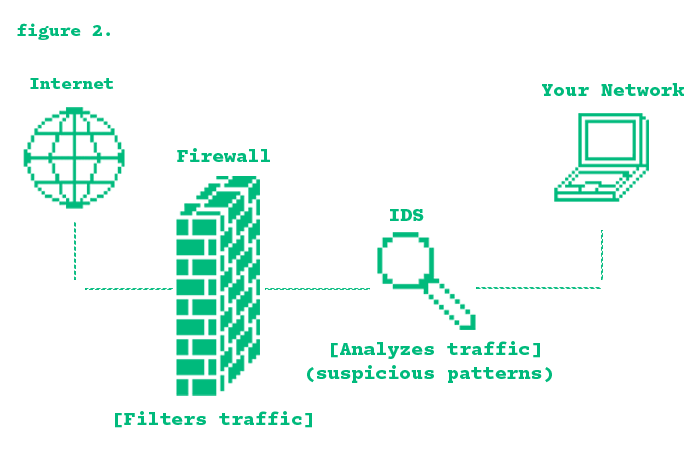
There are also different types of firewalls such as:
Packet-Filtering Firewalls - Packet filters evaluate packet data to carry out firewall operations. Every packet of data that reaches the network edge is separated. It examines individual data packets and decides whether to allow or block them based on predefined rules (IP address, port, protocol). Although it is fast and lightweight, it lacks deep inspection (can't analyze packet contents).2
Stateful Packet Inspection Firewalls - Early firewalls used static rules to allow or block packets based only on factors like IP address, port number, and protocol. However, they couldn’t track whether a packet belonged to a valid, ongoing connection. This made them vulnerable to attacks like DDoS amplification, where a victim is flooded with unsolicited responses from legitimate services. A stateful inspection firewall (also called a stateful firewall) doesn’t just look at individual packets—it keeps track of active connections and only allows responses that match a valid request. SPI’s offer dynamic packet filtering, scalability and performance, logging and monitoring, and security integration.3
Dynamic Packet Filtering: The main differentiating feature between stateless and stateful firewalls is dynamic packet filtering. The ability to track the state of a network connection and permit or block packets based on it enables these firewalls to identify malicious traffic that a stateless firewall would miss.
Scalability and Performance: Performing stateful inspection of network traffic requires more resources than a stateless firewall. SPI firewalls should have the resources required to analyze and secure corporate network traffic at scale while minimizing latency and performance impacts.
Logging and Monitoring: Firewalls have vital visibility into the traffic attempting to enter or leave an organization’s network. SPI firewalls should provide logging and monitoring capabilities to enable security teams to detect attempted intrusions.
Security Integration: Firewalls are one component of a corporate security architecture. They should integrate with other security solutions to enhance threat prevention capabilities and simplify security management.
Proxy Firewalls (Application-Level) - Proxy firewalls operate at the application layer, filtering traffic between the network and external sources. Instead of allowing direct communication between a client and a server, they act as an intermediary (proxy) to inspect all incoming and outgoing data. Proxy firewalls operate at the application layer, filtering traffic by acting as an intermediary between the network and external sources. Instead of allowing direct communication, they establish a connection, inspect the TCP handshake and packet contents for threats like malware, and only forward approved data. By masking internal devices, proxy firewalls enhance security and anonymity. However, their deep inspection process can slow down data transfer. Positioned at the network edge, they analyze application protocol headers and payloads to decide whether to permit or block data, offering stronger protection than traditional firewalls.4
For reference, when we say a security mechanism operates at the application level, we mean it functions at the Application Layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model. This is the topmost layer where human-computer interactions happen, and applications can access network services.
Next Generation Firewalls - A Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) enhances traditional firewall capabilities by integrating intrusion prevention, malware filtering, and advanced traffic control. Unlike conventional firewalls that primarily examine network ports and protocols, NGFWs focus on applications and data by deeply inspecting packet payloads before deciding whether to allow or block traffic. A key feature of NGFWs is Application Intelligence, which enables them to identify specific applications within network traffic, regardless of port, protocol, or evasion techniques. This deeper level of security provides greater control and protection against modern cyber threats.5
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) monitors network activity to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. It analyzes traffic without interfering, alerting administrators to suspicious behavior.
Intrusion detection involves monitoring and analyzing events in a computer system or network to identify attempts to compromise its confidentiality, integrity, or availability, or bypass security measures. These intrusions can come from external attackers, authorized users trying to gain unauthorized privileges, or those who misuse their granted access. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs) are tools—either software or hardware—that automate the monitoring and analysis process to detect such suspicious activities.6
Having an IDS and a firewall on a network can add extra network security because of how they complement each other. While a firewall acts as the first line of defense by blocking unauthorized traffic, an IDS works alongside it by analyzing that traffic that passes through, identifying suspicious activity.
The firewall follows the network's security rules, allowing or blocking data passing through based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols. But firewalls do have they're limits. They're unable to inspect the incoming traffic deeply for anything suspicious/malicious. Meaning malware can possibly enter.
Now its the IDS's job to analyze the traffic that passes through the firewall. It examines patterns to recognize malware, brute force attacks, or unusual data transfers. Once malicious behavior is detected, it can take the necessary precautions to document it and alert administrators.
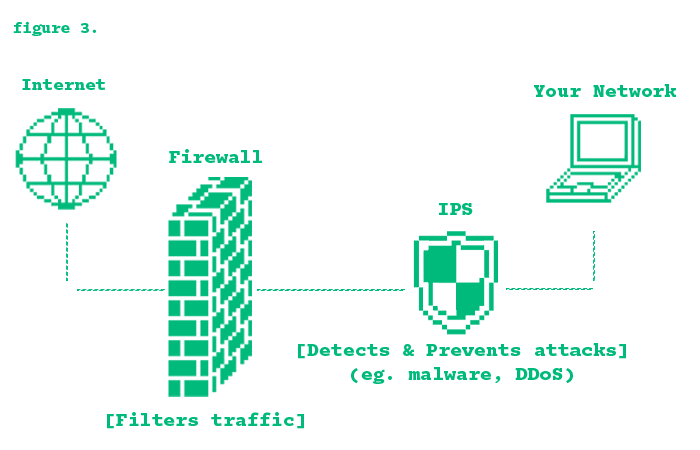
You can see how a firewall alone may not detect attacks that exploit legitimate traffic. But when paired with an IDS, it identifies those hidden threats. Now it doesn't really have to go in that order. It could be the IDS goes first and inspects the traffic, and then it goes through the firewall. But I feel it makes much more sense for it to go after the firewall.
Many Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs) are built around three core components: Information sources, analysis, and response. Information sources are the various sources of event data used to determine if an intrusion has occurred. Common sources include network, host, and application monitoring. Analysis is the process organizes the data from information sources to identify potential intrusions. The two primary analysis methods are misuse detection, which looks for known attack patterns, and anomaly detection, which flags unusual behavior. And finally response is where once an intrusion is detected, the system takes action. Active measures involve automated responses (such as blocking traffic), while passive measures involve generating reports for human review, who then decide on further actions. These responses are all seperate and not a built-in function with intrusion detection systems.
An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is like a proactive security guard for your network. It actively scans traffic for
malicious activity, stopping threats before they can cause harm. This helps reduce the workload for security teams by
attacks before they even reach the network defenses. And unlike an Intrusion Detection System (IDS), which just watches
and alerts, an IPS sits directly in the traffic path to take action in real-time. Usually placed just after the firewall,
it examines incoming traffic and can block harmful data, issue alerts, block suspicious sources, or even reset connections
to prevent further attacks.
IDS vs IPS? I'd honestly think that IPS is a much better option. It combines the knowledge of IDS in an automated manner.
Not only will it detect malicious patterns, but take the necessary actions to prevent them. It can even alert secruity teams.
An IDS is only for detecting and monitering intrusions. It won't take any action on its own.
Not only that but an IDS needs help from a human, or a seperate automated system to interpret the results.
An IPS can decide whether to accept or reject packets (based on rules). Although both analyze traffic and compare it to known
threats, I believe that IPS is a much better option for network security.7
To keep things running smoothly, IPS systems use techniques like signature-based detection, anomaly-based detection, and stateful protocol analysis. Modern IPS tools are often part of next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) and cloud security services, adding an extra layer of protection to keep your network safe.
Signature-based detection - Signature-based detection works by comparing observed events to pre-defined patterns, or
"signatures," of known threats. It’s fast, easy to set up, and excels at identifying known attacks. However, it struggles
with new or modified threats, especially those using evasion techniques, making it less effective against unknown or
variant attacks. Despite these limitations, a signature-based IDS can still be highly accurate when it comes to detecting
recognized threats.
Anomaly-based detection - Anomaly-based detection involves comparing observed activity against predefined profiles of "normal" behavior, such as
typical user actions, network connections, or application usage. These profiles are created by monitoring standard activity
over time. The main advantage of this technique is its ability to identify unknown or unusual threats. For example, an
anomaly-based IDS might flag a malformed IP packet as suspicious, not because it matches a known attack pattern, but
because it deviates from expected behavior. This makes anomaly-based detection effective at spotting new or unexpected
types of malicious activity.
Stateful protocol analysis - Stateful protocol analysis involves comparing observed network traffic against predefined profiles of normal
behavior for each protocol state. It looks for deviations from accepted patterns to identify potential threats.
While it shares similarities with anomaly-based detection, stateful protocol inspection goes further by analyzing
traffic at the network and transport layers, as well as vendor-specific traffic at the application layer—areas that
anomaly-based detection typically cannot examine. This makes stateful analysis a more comprehensive approach to
detecting unusual traffic.
Next time when discussing network security, tools like firewalls, IDS, or IPS should come in mind. These mechanisms form the backbone of strong network architectures, each serving a unique purpose in protecting data, systems, and users from threats that continuously evolve. Whether it's blocking unauthorized access, identifying suspicious activity, or preventing harmful traffic, they work together to build a layered and secure defense.